Choosing an LMS shouldn’t feel overwhelming, but for most teams, it does. Every vendor promises the perfect solution, demos look impressive, and yet the real challenges show up later: unexpected costs, complex workflows, and slow rollouts that stall training.
Buyers aren’t confused. They’re exhausted. As one put it, “Every vendor says yes to everything, and I don’t know who to trust anymore.”
This guide cuts through that noise. It’s a clear and practical way to select an LMS that truly fits your team’s needs.
What this guide covers
- A quick breakdown of the different types of LMS platforms
- The essential steps to choosing an LMS that fits your needs
- The features that matter most (and which ones you can ignore)
- Common challenges teams face during LMS selection
- Practical strategies to compare vendors and make a confident choice
Let’s get into it and figure it all out!
What Is an LMS and Why It Matters
A learning management system is software that helps you create, deliver, and track training in one place. It keeps courses, users, and progress organized so teams don’t rely on scattered files or manual tracking.
Why it matters:
An LMS solves the problems that make training inefficient, such as:
- inconsistent onboarding
- missed certifications
- limited visibility into learner progress
- heavy admin workload
- difficulty scaling training across teams, locations, and devices
Modern platforms also use AI to speed up course creation, personalize learning paths, and flag learners who need support. This turns training into a manageable, continuous process instead of something teams struggle to maintain.
Types of LMS:
Before choosing a platform, it helps to understand how LMS systems differ. The main categories are:
- SaaS (Cloud-Based): Subscription-based, quick to deploy, automatically updated, and requires minimal IT involvement.
- On-Premise: Installed on your own servers with full control over data and customization, but with a higher upfront cost and ongoing maintenance.
- Open-Source: Free to download and flexible, but requires developers, plugins, hosting, and security management. Costs rise quickly without in-house technical support.
- Custom-Built: Designed from scratch for very specific needs, but the most expensive and slowest option with higher long-term risk.
Understanding these types gives you context, but the real selection process starts when you define who your learners are and what outcomes matter to your organization.
Get Clear on Who You’re Training and Why
Before you compare platforms, you need a clear picture of who you’re training and what you want the LMS to achieve. Most selection mistakes happen because teams skip this step and end up evaluating features without context.
1. Know Who You’re Training
Different learner groups have different expectations, and your LMS has to support those differences instead of forcing everyone into the same experience.
You may be training:
- New hires who need a structured onboarding path
- Frontline teams who rely on short, compliance-driven modules
- Sales teams who want quick, mobile-first access to product updates
- Partners or customers who expect a polished, branded portal
- Remote employees who need flexibility across time zones
Understanding these groups helps you determine what the LMS must handle immediately and what can be secondary.
2. Define Clear Learning Goals
Your LMS should support outcomes that matter to the business. Instead of broad goals like “improve training,” outline the specific results you want.
For example:
- Reduce onboarding time
- Automate compliance tracking and renewals
- Give managers visibility into learner progress
- Eliminate spreadsheet-based tracking
These goals become the lens through which you evaluate every vendor.
3. Understand How Your Teams Work
Your environment also affects your LMS needs. A distributed workforce might require multilingual learning and strong mobile support. Different departments may need separate learning paths, permissions, or branded experiences. These practical realities shape what the LMS must deliver as you scale.
4. Clarify Your Content Requirements
Think about the type of content you’ll deliver and how often it needs updating. Videos, documents, quizzes, and SCORM packages all require different levels of support. If you plan to build content in-house, you may need templates, a built-in authoring tool, or AI to speed up creation.
5. Map Out Technical and Integration Needs
These are often discovered too late. If you rely on HRIS, CRM, SSO, or communication tools, the LMS must connect to them cleanly. Modern AI features may also matter if you want automated reminders, personalized learning paths, or early warnings about at-risk learners.
Key Features to Evaluate in an LMS
When you reach this stage, you already know your audiences, your goals, and your non-negotiables. Now the question becomes simple: What features will actually help you deliver the outcomes you care about?
This is where I want you to move past generic checklists and evaluate each feature through one lens: does this make training easier, faster, and more effective for your learners and admins?
a) Ease of Use & Learner Experience
If an LMS isn’t easy to navigate, adoption drops, no matter how advanced the feature list looks. You should expect a clean, intuitive interface that requires no training to figure out. Learners should be able to log in, find their courses, and track progress without friction.
A strong LMS gives you:
- Mobile-friendly access so learning fits into real workdays
- Simple navigation that doesn’t overwhelm new users
- Accessibility support for diverse learners
- Gamification features such as badges, leaderboards, and progress tracking
The goal isn’t just “user-friendly.” It’s zero frustration. When the experience is smooth, completion rates improve without you chasing anyone.
b) Content Management & Learning Paths
This is the backbone of your training strategy. You need an LMS that helps you build, organize, and deliver content quickly, not one that slows you down.
Expect:
- Easy course creation using your existing PDFs, PPTs, videos, and Docs
- Ready-to-use, fully editable courses for onboarding, compliance, and product training
- A strong library of reusable templates so you can build new modules quickly and maintain consistency
- Flexible learning paths that guide different roles through the right sequence
- Scheduled lessons, quizzes, and assessments to structure learning over time
- SCORM/xAPI compatibility so you never get locked into a single vendor
If you can’t build or update content without waiting on someone else, the LMS will fail you in the long run.
c) Integrations & Technical Compatibility
Your LMS should integrate seamlessly with the systems you already use. If you choose a platform that doesn’t integrate well, you’ll end up managing users manually, and trust me, that becomes painful fast.
Look for integrations with:
- HRMS/HRIS for automatic user sync
- CRM tools like Salesforce or HubSpot
- Communication tools such as Microsoft Teams, Slack, or Zoom
- Single sign-on (SSO) for frictionless login
- Secure cloud hosting and APIs that allow your system to grow with you
Integrations eliminate repetitive admin work. Without them, your team will spend hours on tasks the LMS should automate.
d) AI-Powered Features
This is where modern LMS platforms create real advantage. AI isn’t a bonus; it directly impacts how fast you can create content, how personalized the learning becomes, and how little manual effort your admins need to put in.
AI is integrated throughout the entire training workflow, making it easier to build, deliver, and refine learning programs:
- AI Course Builder: Instantly convert PDFs, PPTs, or Docs into structured, ready-to-train courses.
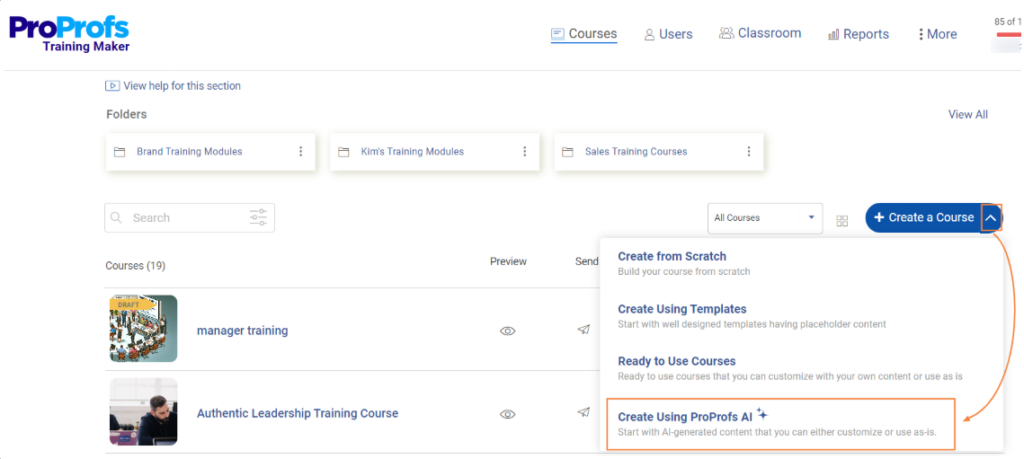
- Personalized Learning Paths: Courses auto-assigned based on role, performance, or past progress.
- Automated Admin Tasks: Enrollments, reminders, certifications, and renewal alerts, all handled for you.
- Predictive Analytics: Spot skill gaps and identify at-risk learners before performance drops.
- Multilingual Learning: AI adapts content for global teams without requiring your team to rebuild it manually.
In simple terms: AI cuts your workload, boosts learner engagement, and helps you scale training without extra headcount.
e) Reporting & Analytics
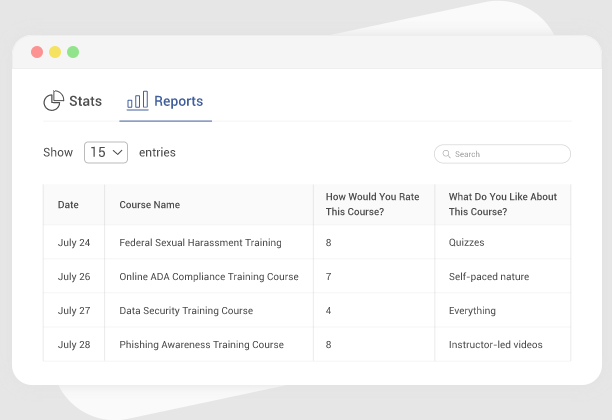
If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it. Reporting is where most LMS platforms overpromise, so this is an area where you need to be strict.
Expect:
- Real-time dashboards that highlight risks and progress
- Customizable reports you can tailor to departments or leadership needs
- Insights into engagement, completion, skill development, and training ROI
You should be able to answer questions like:
Are new hires onboarding faster? Which teams need support? What’s the real business impact of our training programs?
How to Choose an LMS: Step-by-Step Process
Selecting an LMS can feel overwhelming with so many platforms in the market, but the right one can transform how you deliver training. This step-by-step process will help you make a confident decision based on your goals, team size, and long-term learning needs.
1. Define Your Needs and Shortlist 3 – 5 Vendors
Start by assessing your organization’s requirements. Consider factors like user volume (e.g., 50 employees vs. 5,000), integration needs (with HR tools like Workday or video platforms like Zoom), and specific features such as mobile accessibility or gamification. Create a must-have list. Do you need multilingual support or certification tracking? Use resources like G2 or Capterra to research vendors. Narrow to 3 – 5 based on reviews, market share, and scalability. For instance, if AI-driven personalization is key, prioritize platforms like Docebo or 360Learning.
2. Request Demos or Free Trials
Once shortlisted, contact vendors for personalized demos or free trials (most offer 14 – 30 days). Prepare targeted questions: How does it handle custom branding? What’s the uptime guarantee? During demos, involve stakeholders like IT, HR, and end-users to simulate real workflows. Trials let you upload sample content and test integrations hands-on, revealing hidden friction points early. This stage strengthens your LMS selection decisions with real user experience data.
3. Evaluate User Experience, AI Tools, and Reports
Dive into core functionalities. Assess user experience (UX) for intuitiveness; clunky interfaces lead to low adoption. Test AI tools like adaptive learning paths (e.g., recommending courses based on performance) or chatbots for learner support, which boost engagement by 20–30% per industry benchmarks. Scrutinize reporting: Look for customizable dashboards tracking completion rates, skill gaps, and ROI metrics. Ensure compliance with standards like GDPR or SCORM for secure, interoperable data. These factors are key when selecting an LMS that can scale with your organization.
4. Factor in Budgeting and Pricing Models
Cost is a make-or-break element often overlooked. Allocate 5 – 10% of your training budget to LMS expenses, factoring in setup, ongoing fees, and support. Common pricing models include:
- Per-user/subscription: $5 – $20 per active user monthly (ideal for growing teams; scales with usage but can spike).
- Flat fee: $2,000 – $10,000 annually (best for fixed user bases; predictable but less flexible).
- Per-course or tiered: Usage-based (e.g., $0.50 per learner-hour), suiting variable training volumes.
Hidden costs? Add-ons like premium AI modules or custom development. Negotiate bundles or multi-year discounts to achieve a 15 – 20% reduction. Tools like ROI calculators from vendors help justify spend, and aim for systems to recoup costs via reduced training time. Budgeting is central to smart LMS software selection.
5. Pilot with a Small Team
Select a 20 – 50 user pilot group (e.g., one department) for 4 – 6 weeks. Roll out 2 – 3 courses, monitoring adoption via built-in analytics. Track metrics like login frequency and feedback surveys to gauge fit. This pilot essentially validates the choices made earlier in your LMS selection process.
6. Gather Feedback and Finalize Rollout
Post-pilot, compile insights: What frustrated users? Did reports deliver actionable data? Refine based on input, then scale organization-wide with training sessions and change management. Revisit contracts annually for optimizations.
By methodically following these steps, you’ll land an LMS that enhances learning outcomes without breaking the bank. Expect the process to take 2 – 3 months, yielding a 25%+ efficiency gain in training delivery. These steps serve as a complete, practical approach for anyone researching how to choose an LMS or following a structured LMS selection framework.
Watch: Top 5 Learning Management Systems You’ll Wish You Found Sooner
Get Free LMS Software — All Features, Forever.
We've helped 567 companies train 200,000+ employees. Create courses in under a minute with our AI LMS or use 200+ ready-made courses on compliance, harassment, DEI, onboarding, and more!
5 Challenges to Watch Out for (Learning from Others’ Expensive Mistakes)
Even the most careful LMS selection process can go wrong if you miss common pitfalls. Many organizations learn these lessons the hard way, usually after spending thousands of dollars and months of wasted effort. Here are the biggest red flags to look out for when selecting an LMS.
1. Overpromising Vendors
The Problem: Every vendor says “yes” to everything during sales calls. Features sound perfect until implementation reveals limitations.
The Solution: Do not rely on promises. Ask vendors to demonstrate each feature in a live environment. Request sandbox access and get commitments in writing. During LMS software selection, the question is not whether a feature exists, but whether it works in practice.
2. Hidden Cost Landmines
The Problem: Attractive entry-level pricing such as “$2 per user per month” often excludes critical features, integrations, or support levels. Costs can balloon quickly.
The Solution: Always request a full cost breakdown, including:
- Base platform fees.
- Per-user charges at your projected scale.
Integration and setup fees.
- Ongoing support costs.
- Content migration expenses.
One of the smartest tips in how to choose an LMS is to calculate costs not just for the first year, but for three to five years of usage. This prevents surprises as your training needs grow.
3. Migration Nightmares
The Problem: Data portability is often overlooked until it is too late. One user shared, “Our old vendor held our data hostage during the switch. Took 4 months and legal threats to get our course content back.”
The Solution: Confirm data portability before you sign. Ask whether you can export user records, course content, and completion data in standard formats like SCORM or xAPI. Clarify what migration assistance the vendor provides and whether there are fees attached. Treat migration as a core requirement, not an afterthought.
4. Academic Versus Corporate Mismatch
The Problem: Many LMS platforms began in academic settings and later bolted on corporate features. The result is clunky workflows that frustrate business users. Compliance tracking, reporting, and role-based management often feel like afterthoughts.
The Solution: Focus your LMS selection on platforms designed for corporate learning from the ground up. The difference in workflow efficiency and user experience is significant, especially when scaling across departments or franchises.
5. Post-Sale Support Reality Check
The Problem: Pre-sale support feels attentive and proactive, but once the contract is signed, response times slow and support quality drops.
The Solution: Research the vendor’s support structure in detail. Read recent independent reviews with a focus on support experiences. During shortlisting, ask for references from organizations that have used the platform for at least two years. Their feedback will tell you more about long-term support than any sales demo.
The LMS Selection Endgame: Fit Over Features
The best LMS is not the one with the longest feature list, but the one that actually fits your learners, goals, and culture. I have seen simple platforms transform training because they matched how people work, and I have seen feature-heavy systems fail because no one wanted to use them.
Your LMS selection success comes down to three things: clear requirements, must-have features that solve real problems, and testing vendor claims against your own workflows. Tools like ProProfs Training Maker show how this balance plays out, offering essentials such as compliance tracking, reporting, mobile learning, and course creation without overcomplicating the experience.
Done right, your LMS will not just be software. It will be the foundation for a learning culture that delivers measurable business results. Done wrong, and you will be back at the start of another LMS software selection process sooner than you would like.
The choice is yours. Now you know how to choose an LMS – so choose wisely.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I avoid hidden costs when selecting an LMS?
Ask vendors for a full cost breakdown up front. This should include base platform fees, per-user pricing, setup costs, support packages, and migration expenses. Never settle for vague “starting at” prices. Total cost of ownership is what matters in LMS software selection.
Do I need technical staff to manage an LMS?
Not always. Many cloud-based systems are designed for non-technical admins and include automation for reporting, user management, and content updates. If you are considering open-source or custom-built platforms, you will need IT resources. Knowing this early helps in how to choose an LMS that matches your team’s capacity.
How long does LMS implementation usually take?
It depends on the vendor and your requirements. SaaS platforms can be set up in days or weeks, while on-premise or custom systems may take months. During LMS selection, always ask for implementation timelines and customer references to confirm how realistic those timelines are.
What should I look for in vendor support during LMS software selection?
Look for clear commitments around response times, onboarding help, and long-term support. Community feedback often highlights vendors who disappear after the contract is signed. Strong, transparent support is as important as features when selecting an LMS.


 We'd love your feedback!
We'd love your feedback! Thanks for your feedback!
Thanks for your feedback!