Choosing the right LMS feels like walking through a maze, especially when LMS pricing models are confusing and hidden costs keep popping up. It’s tough to get what you need without overspending. Don’t worry; you’re in the right place.
Here’s the deal: the global LMS market was valued at $20.33 billion in 2023 and is set to grow to a staggering $82 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 17.0%. But even with this growth, more than half of companies still struggle to pick an LMS that fits their needs and budget. Surprising, right?
I’ll break down LMS pricing models in simple terms, give you practical tips to manage your budget, and help you figure out what works for your organization. Make sure you get the most bang for your buck.
Why Is LMS Pricing Important?
When you shop for a phone, do you grab the first one that catches your eye, or do you compare models, features, and prices to get the best deal? The same goes for an LMS. Picking one without understanding its pricing can lead to more problems than solutions. Here’s why LMS cost matters:
- Budget Control: Nobody likes unexpected costs. Knowing the pricing structure helps you avoid surprise fees for extra features, users, or storage. It ensures your LMS stays within budget.
- Choosing the Right Pricing Model: There are multiple learning management system pricing models, and not all are suitable for every business. For example, a per-user model might be more cost-effective if your business is small and just getting started. In contrast, a subscription-based model could be better for larger organizations with ongoing training needs.
- Getting the Right Features: You don’t want to pay for tools you’ll never use. Clear pricing helps you focus on the features that align with your training goals so you’re not wasting resources.
- Scalability: Your needs might grow. A transparent pricing model lets you plan for expansion without worrying about skyrocketing costs.
- Return on Investment: You’re not just buying software but investing in your organization’s growth. Understanding learning management system cost ensures you get the best value and measurable results for your money.
- Avoiding Hidden Costs: Support fees, customization charges, or extra training sessions can add up. Knowing what’s included can help you avoid unpleasant surprises.
Clear pricing isn’t just about saving money but about making smart decisions. It ensures you invest in an LMS that supports your team without breaking the bank.
Common LMS Pricing Models
The costs of LMS software can vary significantly based on several factors. That said, seven standard learning management system pricing models are generally followed across industries.
Here’s a quick look at them:
| Pricing Model | Description | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|
| Freemium | The product is offered for free with limited usage. Users can try it before committing to a paid plan. | Those who prefer to test the waters before upgrading to a paid plan. |
| Subscription- Based |
Recurring fee (monthly/annually) to access the LMS, including updates and support. | Anyone who wants to avoid managing an LMS independently prefers a cloud-based solution. |
| Perpetual Licensing | One-time fee to purchase the LMS, often with limited support and updates. Additional costs for extended support or upgrades. | Organizations needing heavy customization that manage their IT resources and updates independently. |
| Tiered Pricing or Feature-Based | Pricing is based on different tiers, offering varying sets of features. Users can scale up as needed. | Organizations with varying needs and budgets to achieve flexibility as their requirements grow. |
| Pay-Per-Use or User-Based | Costs vary based on the number of active users. Pricing fluctuates depending on usage. | Organizations with fluctuating or seasonal training needs or those who prefer to pay for what they use. |
| Open-Source | Free to use and modify. Customization requires technical expertise for maintenance and support. | Organizations with technical expertise to manage and tailor the system. Ideal for businesses requiring custom features or integrations. |
| Custom Pricing | Tailored to an organization’s unique needs and scale, often combining multiple pricing models. | Large organizations or those with specific, complex needs that don’t fit standard models. |
This table will help you quickly understand the pros and cons of each LMS pricing model and determine which one best suits your business needs.
Factors Affecting Pricing of Learning Management Systems
Understanding what you’re paying for an LMS is essential for making the best decision for your organization. Here are a few factors that affect the pricing of an LMS.
- User count: Think of it like planning a corporate event. The more attendees you have, the bigger the venue you’ll need, and naturally, the higher the cost. LMS providers usually have tiered pricing based on the number of users, so a larger user base often means bigger discounts and higher initial costs.
- Deployment model: Cloud-based LMS solutions have lower upfront LMS costs with monthly rent (subscription fees). In comparison, on-premises solutions might have higher initial setup costs but lower recurring expenses.
- Features and customization: A basic LMS with standard features is more affordable but less personalized. Advanced systems that allow extensive customization can be pricier but offer features that perfectly fit your organization’s needs. Take a look at the features that an LMS should ideally have.
- Integration: This is like ensuring your new software works seamlessly with your existing tools. If the LMS needs to integrate with your HR or CRM systems, additional costs might be involved for these integrations or custom API development.
- Support and maintenance: Some providers offer different levels of support, from basic email support to dedicated account managers and 24/7 assistance. Naturally, the more comprehensive the support, the higher the cost.
- Training and implementation: Just like onboarding new employees, implementing an LMS requires time and resources. Some providers include training as a part of the package, while others might charge extra. It’s important to factor in these costs to ensure smooth system adoption.
- Additional services: AI content development, advanced reporting tools, and analytics can drive up the costs. It’s like adding premium features to your car – nice to have, but you must decide if they are essential for your journey.
So, it’s all about finding the right balance between cost and value, much like any strategic decision in a corporate setting.
Real-Life Examples: Calculating ROI for Internal and External Training Using LMS
1. ROI Calculation for Internal Training
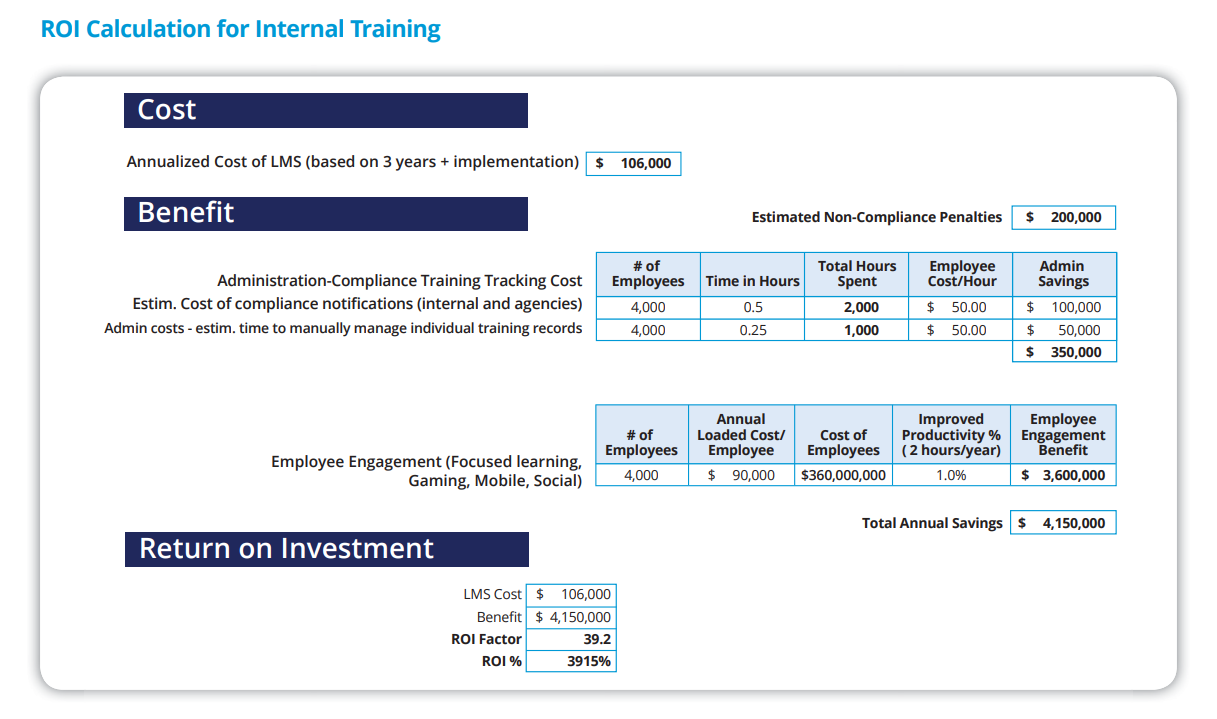
Let me walk you through an example of how one company used an LMS for workforce training and saw a huge ROI. Their main goal was to improve workforce performance, and they aimed for just a modest 1% improvement. Sounds small, right? But it ended up saving them $3.6 million!
Then, they looked at compliance costs. With the LMS, they estimated they could save $350,000 a year by automating the tracking and management of training records instead of doing it manually. That’s a pretty significant amount!
On top of that, they were able to avoid $200,000 in non-compliance penalties—fines that could have easily added up.
In total, they saved $4.21 million, which was over 39 times the cost of the LMS. With those kinds of savings, choosing the LMS was an obvious decision. A superior LMS can pay for itself many times over by improving performance, cutting down on compliance costs, and avoiding penalties.
3. ROI Calculation for External Training
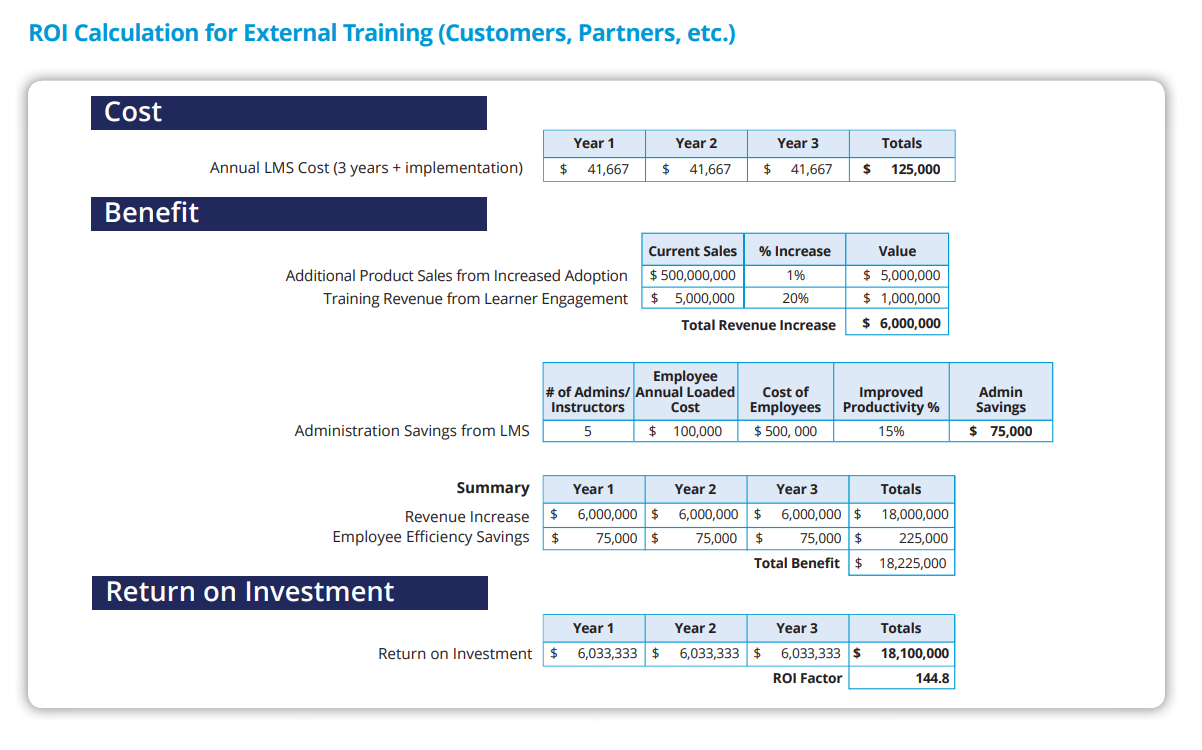
In this example, the company took a more external approach with their LMS, focusing on customer training rather than internal workforce training. The results were impressive, showing a much higher ROI.
The main factor here was the increase in revenue from better-trained customers. With a modest 1% improvement in customer performance, they saw an additional $5 million in revenue each year. This boost in customer training directly impacted repeat sales, as better-trained customers are more likely to return.
But it didn’t stop there. The company also saw a 20% increase in the sale of customer training programs, which generated another $1 million in revenue.
In addition, they projected internal savings from reduced administrative costs, saving $75,000 annually. Employee efficiency improvements added another $225,000 in savings.
When you add it all up, the total benefit came to over $18 million, which is 144 times the actual LMS SaaS pricing. That’s an incredible ROI.
Get Free LMS Software — All Features, Forever.
We've helped 567 companies train 200,000+ employees. Create courses in under a minute with our AI LMS or use 200+ ready-made courses on compliance, harassment, DEI, onboarding, and more!
Tips for Optimizing Your LMS Budget: Cost-Saving Strategies
Here are some proven strategies to optimize LMS budgets:
- Conduct a Needs Analysis: Identify essential features and functionalities to avoid paying for unnecessary extras.
- Leverage Open-Source Solutions: Consider open-source LMS options that can be customized to your needs with lower upfront costs.
- Utilize Bundled Packages: Choose bundled packages that include various tools and services at a discounted rate.
- Negotiate Contracts: Don’t accept the first offer; negotiate for better terms, discounts, or additional features.
- Opt for Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud-based LMS platforms often have lower maintenance costs and scalability benefits.
- Train Administrators In-House: Develop expertise within your team to reduce reliance on external support services.
- Prioritize Scalable Solutions: Select an LMS that can grow with your organization to avoid frequent, costly upgrades.
- Review User Licenses Regularly: Adjust the number of licenses based on actual usage to avoid paying for unused accounts.
- Implement Self-Service Options: Enable users to resolve common issues to reduce support costs.
- Take Advantage of Free Trials: Use free trials to evaluate if the LMS meets your needs before committing.
- Seek User Feedback: Regularly gather feedback to identify cost-effective improvements and necessary features.
- Plan for Long-Term Costs: Consider long-term expenses, including renewal fees, to avoid future budget surprises.
Looking for a cost-effective LMS?
Get started with our cloud LMS for free.
LMS Pricing Examples
I have put together a list of the six most popular LMS vendors and how they set up their pricing. Take a look:
1. ProProfs Training Maker
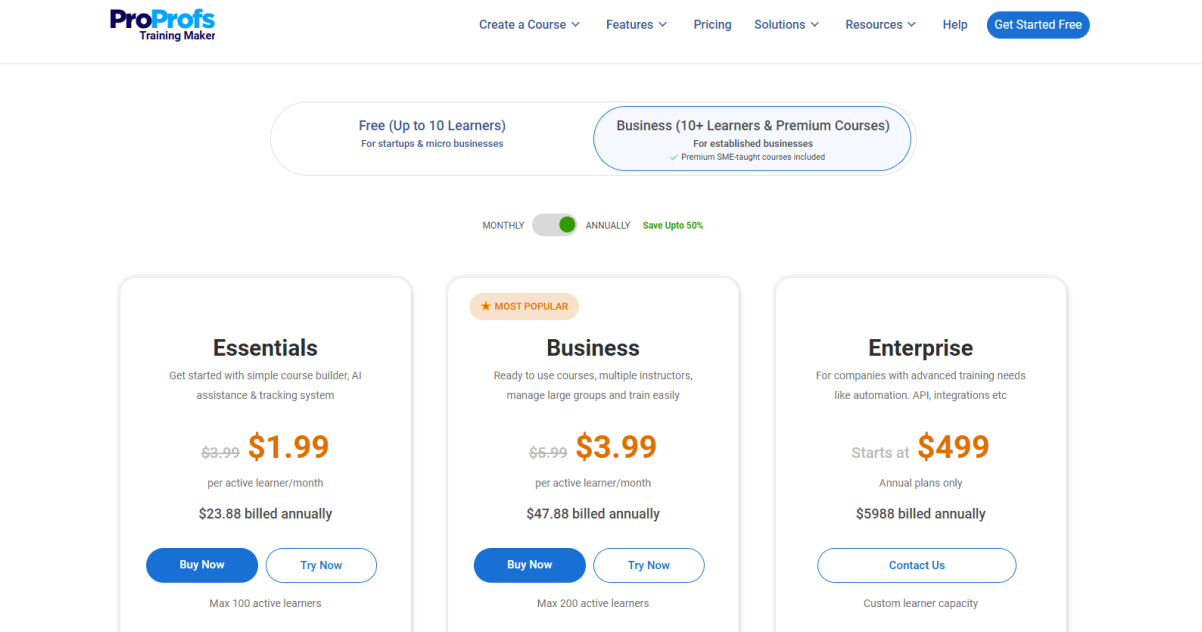
ProProfs Training Maker is an award-winning cloud LMS that follows a subscription-based pricing model. Plans start at $1.99/learner/month and include all the product features, including unlimited courses, unlimited admins, custom certificates, a library of hundreds of premium courses, a dedicated onboarding manager, etc.
It is an AI Learning Management System with which you can create courses in minutes. Just enter your topic and it will convert into a structured course—complete with lessons, quizzes, and multimedia—within minutes.
There are no hidden charges. ProProfs Training Maker offers a forever free plan for small organizations.
You can view this dedicated page to get an overview of its pricing and find answers to relevant queries.
Explore KDD’s success story: How KDD saved their training costs with ProProfs Training Maker. Read Full Story
2. iSpring Learn
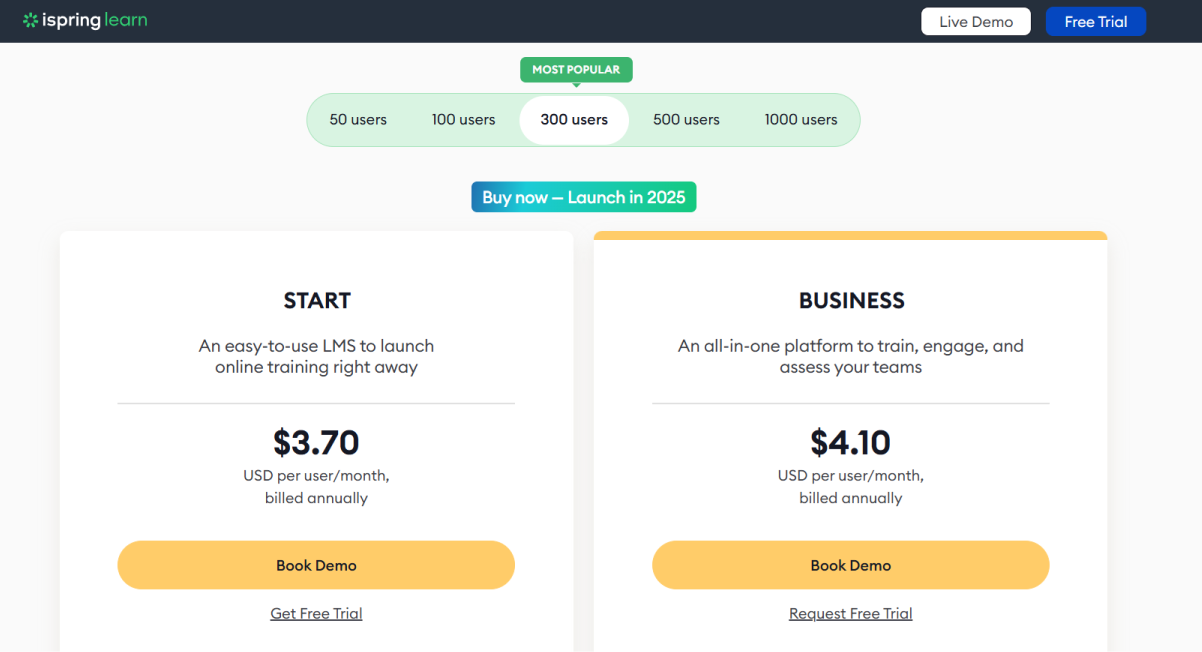
iSpring Learn LMS uses a pay-per-active-user pricing model, which means you only pay for users who log in at least once a month. The cost of this LMS starts at $3.70 per user/month (billed annually), with customized options for larger teams or unique needs.
This model ensures cost-effectiveness by charging based on actual engagement rather than total registered users. For organizations exceeding the user limit, iSpring provides notifications and support to adjust plans.
For more details, please visit this page.
3. LearnWorlds
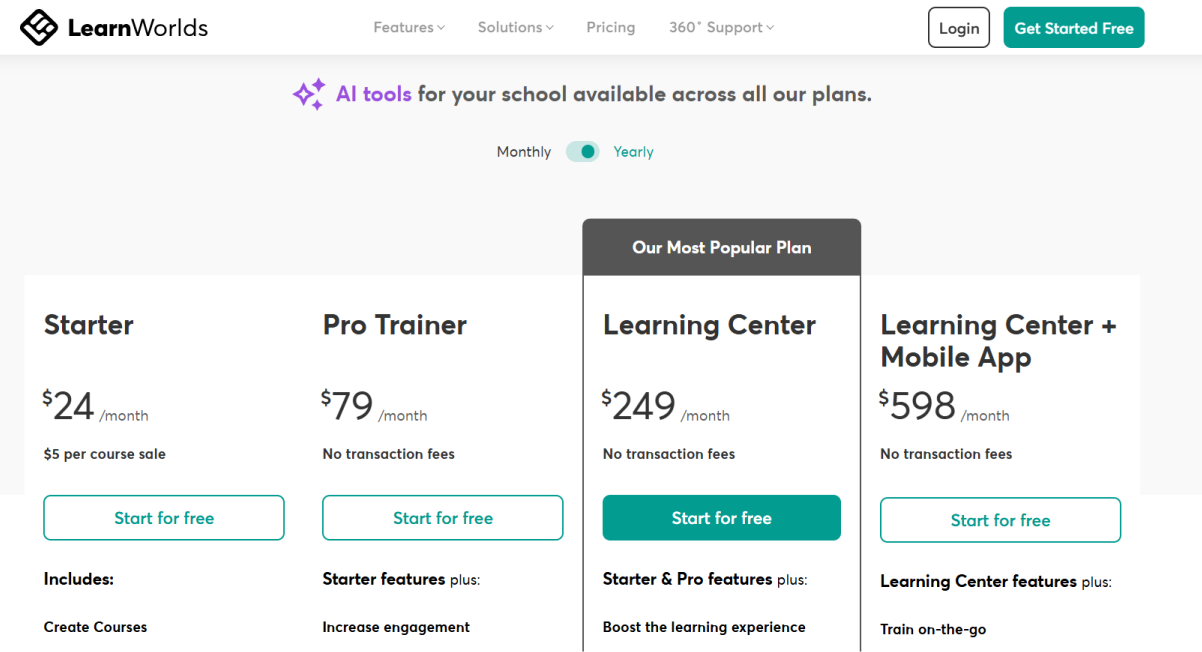
LearnWorlds offers a flexible pricing model with plans for various needs. The Starter Plan ($29/month) suits beginners, featuring unlimited paid courses, a 3-page website, and essential integrations. The Pro Trainer Plan ($99/month) adds live classes, mobile apps, and affiliate marketing, which is ideal for growing teams. The Learning Center Plan ($299/month) includes advanced features like interactive videos, detailed reporting, and automation, perfect for scaling academies.
For mobile-first organizations, the Learning Center + Mobile App Plan ($598/month) provides white-labeled native apps and offline video capabilities. High-volume enterprises can access custom pricing with premium servers and tailored support. All plans include AI tools, robust integrations, and a free trial.
Visit this page to learn more about the pricing.
4. Deel
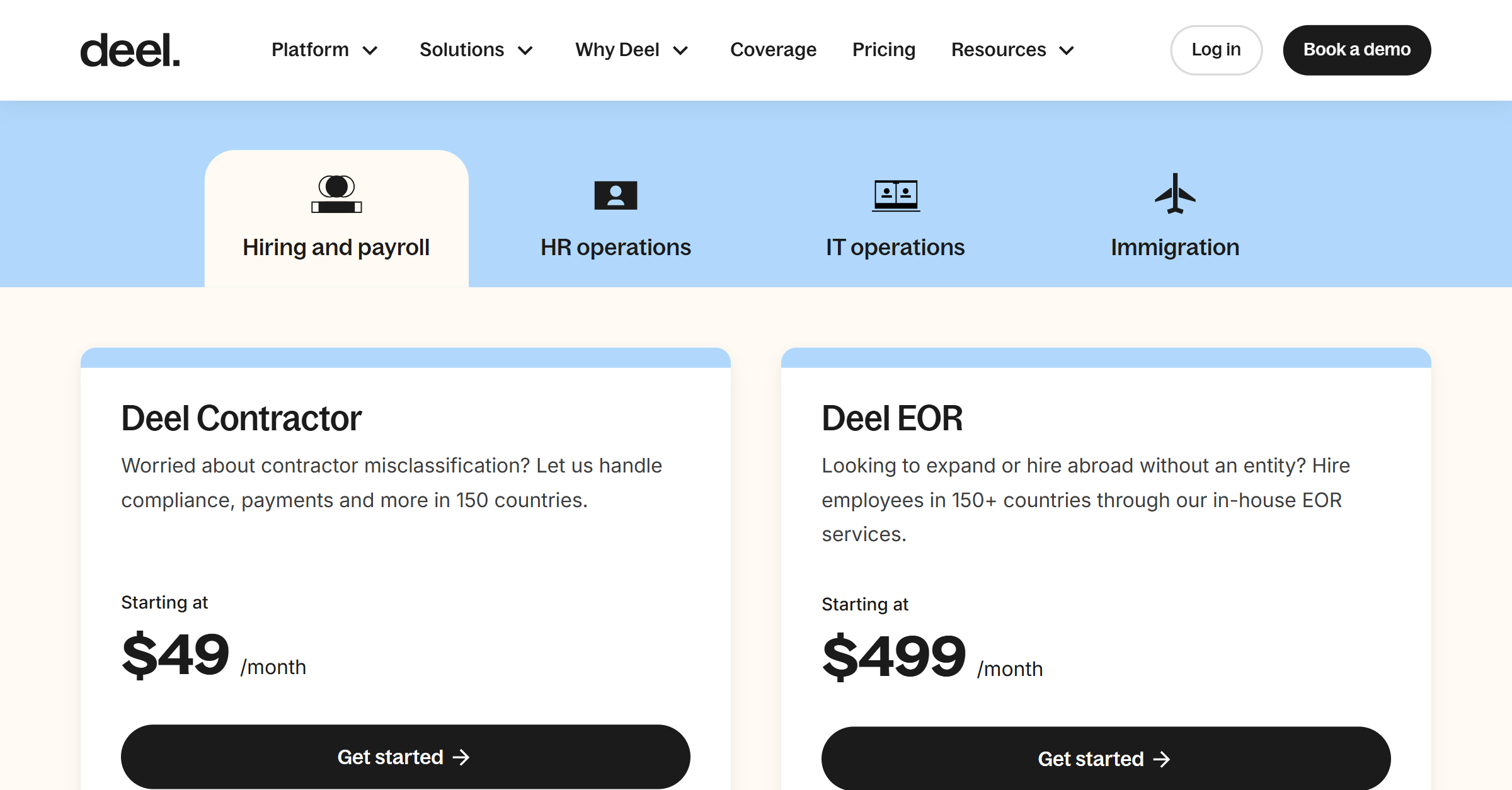
Deel operates on a straightforward, contract-based pricing model, where clients pay based on the number of active contracts they manage each month rather than charging contractors or employees subscription fees. For independent contractors, the pricing is consistent across three contracts—Fixed Contracts, Pay-As-You-Go Contracts, and Milestone Contracts—at $49 per monthly active contract. This fee applies for any month in which work is submitted, an adjustment is made, or a milestone is active.
Deel offers customized pricing for full-time employees, and clients are encouraged to reach out for more specific details. This model provides flexibility, as businesses only pay for active contracts. For more personalized assistance, Deel offers 24/7 support and a dedicated webpage to explore full-time employee pricing.
For more information on the pricing plans, visit this page.
5. Moodle LMS
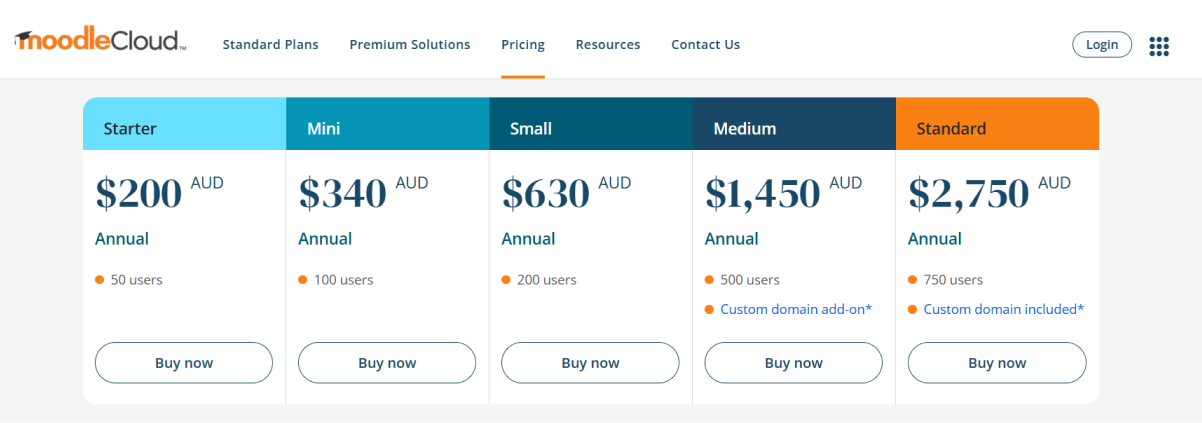
Moodle is an open-source LMS with easy-to-use hosting plans. Known for its flexibility and customizability, It supports dynamic learning experiences while offering affordable pricing for its cloud solutions.
The Standard Plans start at $130/year for 50 users and scale to $1,800/year for 750 users, with features like unlimited courses, integrated video conferencing for 100 participants, and cloud storage through Google Drive and Dropbox. For personalized setups, Moodle’s Premium Hosting connects you with certified partners for tailored LMS solutions. The starter plan also comes with a trial plan!
Check out the plan here.
So, I’d say that an LMS price comparison is a must to ensure you choose the most cost-effective solution that aligns with your training needs and delivers the best ROI.
Ready to Invest in the Right LMS?
Choosing an LMS is a big decision with long-term implications for your organization. It’s not just about the price tag but about finding one that fits your needs, budget, and goals. By understanding the different LMS pricing models and the factors that influence cost, you can make an informed decision that sets you up for success.
Remember, the best LMS isn’t always expensive or the cheapest. It’s the one that aligns with your specific requirements and helps you achieve your training objectives. Take your time, explore your options, and don’t hesitate to ask questions. With careful consideration and a clear understanding of your needs, you can find an LMS that delivers a strong return on your investment and empowers your organization to thrive.
Frequently Asked Questions on LMS Cost
What is the average cost of an LMS?
The average cost of an LMS varies widely, typically ranging from $1.5 to $20 per user per month for subscription models. Custom solutions or enterprise-grade systems can cost thousands annually, depending on features and scale.
Is a custom LMS worth the investment for my organization?
A custom LMS is worth it if your organization has unique training needs or compliance requirements. While upfront costs are higher, the tailored features can deliver greater efficiency and learner engagement over time.
Is a subscription-based LMS better than perpetual licensing?
Subscription-based LMS models are more flexible and scalable and offer regular updates and support. Perpetual licensing may suit those needing long-term cost control but lacks the adaptability of ongoing improvements.
Can I customize an open-source LMS for my organization?
Open-source LMS platforms like Moodle can be customized to suit organizational needs. However, customization requires technical expertise and ongoing maintenance, which could increase the total cost of ownership.
How do I calculate the ROI for an LMS?
Calculate LMS ROI by comparing the total investment (software, implementation, and maintenance costs) with measurable outcomes like reduced training expenses, improved learner performance, and faster onboarding times.
Are there hidden costs when purchasing an LMS?
Hidden costs often include setup fees, customizations, integrations, extra storage, ongoing support, and user training. Carefully review pricing terms and ask vendors for a transparent breakdown.
What’s the difference between free and paid LMS solutions?
Free LMS solutions can include open-source platforms or free plans from vendors. Open-source options allow customization but need technical expertise, while free plans often limit features and scalability. Paid LMS systems provide comprehensive features, support, and scalability at a cost.
 Tips
Tips
We’d love to hear your tips & suggestions on this article!
Get Free LMS Software — All Features, Forever.
We've helped 567 companies train 200,000+ employees. Create courses in under a minute with our AI LMS or use 200+ ready-made courses on compliance, harassment, DEI, onboarding, and more!

 We'd love your feedback!
We'd love your feedback! Thanks for your feedback!
Thanks for your feedback!